Summary:
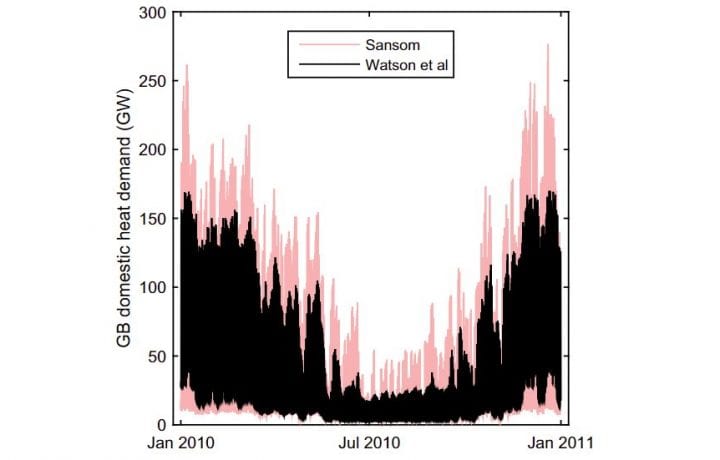
- New findings confirm the impact of large scale heat pump deployment on the grid are far less profound than previously assumed.
- Previous figures used to informing future GB and UK domestic heating scenarios overestimated peak demand and maximum ramp rate.
- The development of more accurate estimates of half-hourly domestic heat demand provides greater clarity and accuracy on the impact of heat pumps.
Read the full article at KENSAHEATPUMPS.COM
A new report published in the international peer-reviewed journal, Energy Policy, Decarbonising domestic heating: What is the peak GB demand?, challenges previous findings about peak demand and maximum ramp rates as a consequence of large scale heat pump deployment, concluding that the electrification of domestic heating is less problematic than assumed.
Kensa’s Contracting Director, Dr. Matthew Trewhella, comments on the reports findings:
This report increases confidence that the UK can meet it’s carbon reduction targets via the electrification of heat through the use of ground source heat pumps. Unlike direct electric, heat pumps produce more heat than the electric that they consume which will reduce the load imposed on the grid. When using ground source heat pumps, this strain is further reduced because ground source heat pumps are typically 20-25% more efficient than air source heat pumps.